- A symphony is a sonata written for an orchestra.
 Bueno, como no podía ser de otra manera y para concluir llegamos a sexto.
Bueno, como no podía ser de otra manera y para concluir llegamos a sexto.Este año navegaremos por la historia de la música descubriendo como hemos cambiado y como la música nos ha venido acompañando con los años.
Aquí os dejo algún que otro video que es más que ilustrativo.
 Erase una voz... la música --> Recorrido de la música vocal con un toque de humor.
Erase una voz... la música --> Recorrido de la música vocal con un toque de humor.Historia de la música (lecciones ilustradas)
Recorrido rápido y breve en un solo dibujo.
Barroco y Clasicismo
UNIT 1: MUSICAL PROTAGONISTS
The protagonists are the main characters in a film or story. In music, many of the protagonists study at specialist schools, including music conservatories. They learn to compose, conduct, play, sing teach and research music.
MUSIC PROFESSIONS AND PROFESSIONALS
From the time the composer writes a piede of music until it reaches the audience, many different music professionals work on it, including performers, arrangers and music producers. There are also other music professions related to research and teaching.
Creating, research and teaching.
- A composer creates works of music. Instrumentalists, singers and conductors perform them at concerts or record them. Sometimes, one person alone performs all of these activities.
- Researchers and musicologists analyse and study music.
-Educationalists recommend the best ways of teaching music to teachers.
Editing, recording and distribution.
- Music publishers produce scores and music books.
-Record companies are responsible for recording the music.
-Arrangers and music producers make sure the sound is as good as it can be.
-Music reaches the audience in different ways: through concers, the media (tv, radio, internet,etc..), libraries and music shops.
-Disc jockeys, or DJs, combine and play recorded music and their own creations for the audience.
The Origin
of Music, the Ancient and Middle Ages
Since remote, historical times, man
has made music to express his feelings and to communicate with the force of
nature.
Since man’s first musical
expression, music has developed greatly thanks to the many different civilizations
that existed in the past. We know, for example, that the Ancient Egyptians sang
and played instruments in their ceremonies. In Ancient Greece, the philosopher
and mathematician Pythagoras discovered that music and mathematics are
closely linked when he realized that the sounds on a musical scale are related
arithmetically and he discovered the concept of harmony. The Romans also
developed musical instruments for their large army of soldiers.
The Middle Ages
Profane Music à In the Middle Ages, while religious
music was becoming more important in the monasteries and churches, a new kind
of music was developing in villages and castles. This new music was not
religious and people entertained themselves singing and dancing while minstrels
and troubadours became very popular.
 The
minstrels were not
educated people, they sang but they didn’t know how to compose, so they
interpreted the songs that other people did. They travelled from village to
village offering their repertoire and they were often accompanied by jesters
and jugglers to make their representations more fun.
The
minstrels were not
educated people, they sang but they didn’t know how to compose, so they
interpreted the songs that other people did. They travelled from village to
village offering their repertoire and they were often accompanied by jesters
and jugglers to make their representations more fun.
The
troubadours were educated
musicians from noble families that composed their own music. The 13th
century Spanish king Alfonso X and the 12th century English
king Richard the Lionheart were famous troubadours.
Religious Music à People started writing music in a very basic
form in the Middle Ages. In the monasteries the monks interpreted this music
together and they all sang the same melody. This kind of music is known as Gregorian
Chant which is a form of monophonic liturgical music named after Pope
Gregory the Great. As the techniques for writing music improved, the monks
organized their music on lines and created signs to represent the height of the
sounds they had to sing. This way, the first stave was created by a monk. It was
Guido d’Arezzo who gave each musical note a name
.
.
UNIT 2: SINGING, PLAYING AND DANCING.
Movement is closely related to sound and music. Instrumets and voices produce sound through vibrations, which are small movements. And listening to good music makes us want to move our bodies. The performing arts are artistic activities which combine singing, speaking and instruments with dance.
Music and dance for stage.
The performing arts are theatrical performances. They can combine vocal and instrumental music with dance. The main types are opera, zarzuela, oratorio, ballet and musicals.
Dance
-Dance suites: (16th-17th centuries) were collections of music for four dances. Over time, they developed into the movements of a symphony.
-Ballet or classical dance (18th-19th centuries) is a type of performance that tells a story through dance.
-Modern dance (20th - 21th ceturies) uses freer movements than classical dance.
Other performing arts
Some musical genres combine singing, orchestral music, theatre and dance.
-Opera is a play where the actors sing, accompanied by and orchestra. It first appeared in Italy in the 17th century.
- Oratorio is similar to opera, but the subject matter is religious.
-Zarzuela is a play that has a combination of singing and speaking. It is a Spanish genre of comic opera, also known as light opera.
- Musicals are modern genre of plays or films that combine singing with acting. They use popular music.
The Renaissance
This
artistic period spanned from 15th to 16th century. It
began in Italy and its name for this period (Renaissance) is a
French word which means "rebirth". This period was called the
"rebirth" because many new types of art and music
were reborn during this
time. New social groups developed as merchants who became an upper middle
class.
During
this period, there are new musical developments as Polyphony (varias voces que
suenan o cantan a la vez). In Renaissance kings, the noble class and anybody
with enough money often had their own music group in their castles and homes.
Families became rivals to see who had the best group of musicians or artists.
There was also plenty of music not
written for the church, such as Madrigal (vocal music composition popular among
the young people. Popular instruments during the Renaissance included the “viola da gamba” (a string instrument played with a bow), lutes (a plucked stringed instrument that is a little like a guitar), and the virginal, a small, quiet keyboard
instrument. Also some
other interesting instruments appeared as vihuela, “sacabuche”, “chirimía”, “salterio”,
“serpentón”…
Some
important Spanish musicians were Juan
del Encina and Tomás Luis de
Victoria.
The Baroque
This
period started in Italy in the 17th century (1600) because of the
apparition of the first Opera and spread through most of Europe until 1750.
During this time, the European population lost confidence in many aspects of
life, the fear of death made people more religious and the clergy gained respect
and importance.
 At the
same time, polyphony continued to be the most important musical form in
religious music. However, the clergy also decided to make changes creating the
cantata and the oratory which consisted of vocal and instrumental parts to
interpret religious texts. Some of the most important masterpieces are the
“Passions” that were composed for Holy Week and written by the most outstanding
Baroque composers: Georg Friedrich
Haendel and Johann Sebastian Bach.
At the
same time, polyphony continued to be the most important musical form in
religious music. However, the clergy also decided to make changes creating the
cantata and the oratory which consisted of vocal and instrumental parts to
interpret religious texts. Some of the most important masterpieces are the
“Passions” that were composed for Holy Week and written by the most outstanding
Baroque composers: Georg Friedrich
Haendel and Johann Sebastian Bach. bach cello suite no. 1 prelude
Aleluya (Haendel)
Tones and semitones.
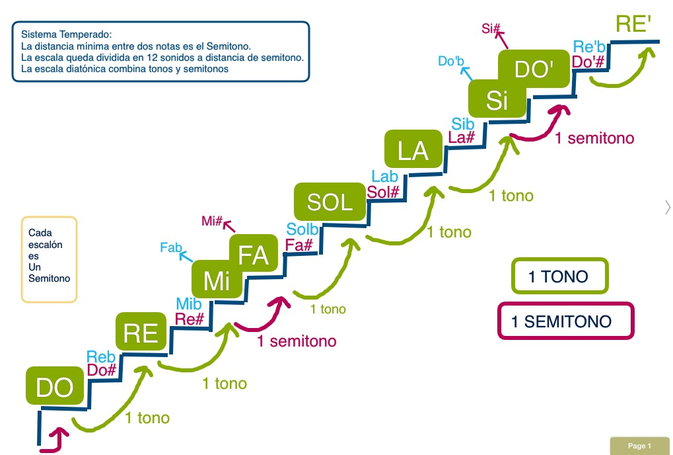
UNIT 3: VOCAL MUSIC
Singing has always been part of every culture. We use it to express feelings and ideas. Songs have evolved. Originally, they had only one part, or voice. Then they were performed by more peple. This led to new concepts such as key and harmony, which changed music.
Singing can have one voice, or part (monophony) or several voices, or parts (polyphony). Vocal music can be religious or non-religious. Non- religious music is also called profane music.
Monophony and polyphony
- Monophony is singing in a single part. This was the type of singing used by medieval monks (the Gregorian chant), minstrels and troubadours. The last two sang profane compositions in cities, castles and palaces.
- Polyphony is several melodies sung at the same tiem. It developed extensively during the Renaisssance (15th and 16 th centuries). First people sang in two parts, then more parts were gradually added.
Accompanied monody
- Accompained monody appeared in the 16th century. It follows the rules of harmony, which is related to key and tonality. This type of music led to great developments in instruments.
- Contemporary classical vocal music is less concerned with the rules of harmony. Compositions are freer. However, popular music still uses classical tonality.
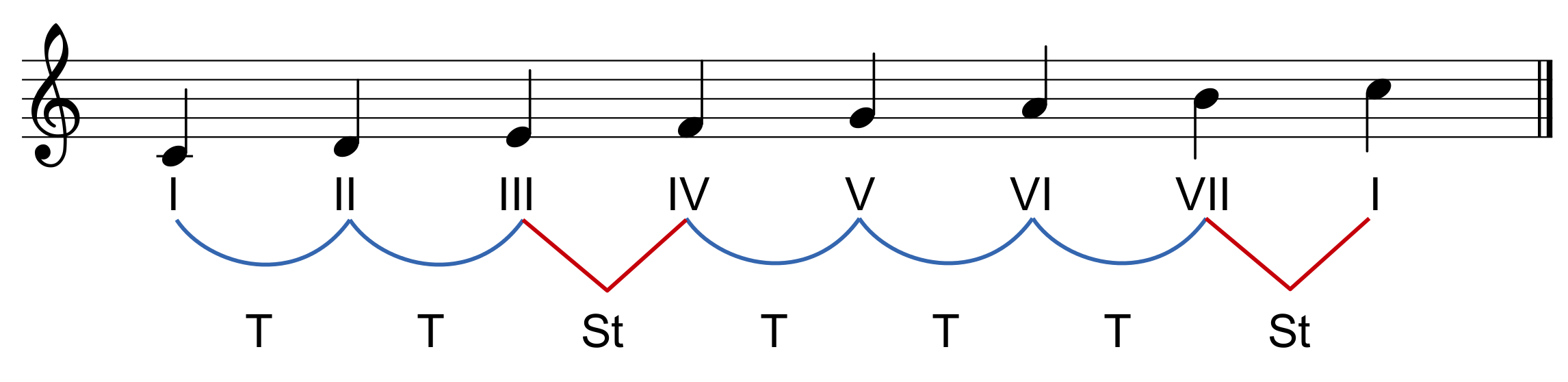
Scales and degrees
Scales are organised groups of notes. The positions occupied by these notes are called scale degrees. The degrees are numbered from one to seven using Roman numerals.
The first degree is called the Tonic. It gives the name to the scale.
It there is a semitone between degrees III - IV and degrees VII-I and a tone between the other degrees, it is a major mode.
Carnival music
Carnival is one of the happiest and most popular festivals
in Andalucía. People dress up, sing coplas
and express their self-confidence and sense of humour.
·
Carnival
is celebrated before Holy Week, in February or March. There are Carnival
celebrations all over the world. In Spain, two of the most important are in
Isla Cristina (Huelva) and Cádiz.
·
Carnival coplas have a wide variety of melodies.
Most of the time, the lyrics to these coplas
express criticism of current problems. Others say positive things about the
place where they are from.
|
During
Carnival, Andalusians sing together in a variety of different groups. The
most popular types are choruses, comparsas,
murgas o chirigotas and quartets.
|
|
Choruses
This is the largest type of Carnival singing
group. They can have up to 45 members. The instruments they normally use
are the guitar, lute and bandurria. The most typical type of copla they sing is the tango.
|
|
Chirigotas
These groups are called either murgas or
chirigotas, depending on the place. They play the same instruments as
comparsas but they have fewer members. One of their most important features
is their sense of humor.
|
|
Comparsas
These groups usually have about 15 members,
although this varies from place to place. They play guitars, the bass drum
and cymbals, snare drum and pito de
caña. Comparsas performs a rich variety of music.
|
UNIT 4: INSTRUMENTAL MUSIC
Until the 17th century, instrumental music was only used to accompany songs and dances. In the following centuries, it expanded considerably. Music was written for just instruments and new ones like electrophones appeared.
Acoustic and electric music
Music played on non-electric instruments is called acoustic. But in electric and electronic music, electricity is required to produce sounds.
Acoustic music
Acoustic music was very important in the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries. Composers wrote many different types or genres of instrumental music:
- A sonata is played by one, two or three instruments.
- Concertos are works for one or more soloists and an orchestra.
Electric and electronic music
In the 20th century, many composers began writing their works in music studios and using recordings.
New instruments were created (electronic instruments) and traditional instruments were adapted (electric instruments).
With the rise of computers, digital sounds and instruments and MIDI appeared. Both composers and music enthusiasts use them.
Classical Period
The Classical Period spanned from the middle of the 18th (1750) to the beginning of the 19th century. During
this period of time, the nobles and upper middle class achieve more power than
in previous period until finally, new political movements such as the French
Revolution fought in favour of freedom.
Profane music
Music was really important.
Composers created new musical forms and investigated new styles. The orchestra
was consolidated (40 musicians and conductor).
The most important musical forma was
the Sonata (three parts).
The symphony
became very popular too. It is a composition for orchestra divided in four
movements and where the first movement or introduction is always in sonata
form.
The Austrian composer Franz Joseph Haydn wrote as many as one hundred and four symphonies: The Surprise, The Farewells, The Clock…. Another Austrian composer, Wolfgang Amadeus Motzart is considered one of the most important in the history of music. Amongst his works we can find
Religious music
Composers in this period found
inspiration in the old oratorios and in the Baroque composers. Haydn and Motzart were inspired by Haendel.
Mozart’s last composition The Requiem
Mass in D minor was based on the Catholic texts for funeral celebrations.
It is known as one of the most important masterpieces in history.
UNIT 6: MUSIC TODAY
Music has changed a lot since the start of the 20th century. Many composers use rules other than tonality and harmony. New instruments and musical styles have been invented. Cinema, television and the Internet have opened up new channels for music.
THE MUSIC AROUND US
Contemporary classical music
- Nationalism. Inspired by the traditional music of each country or region.
"Fuego fatuo" by Manuel de Falla
- Dodecaphony. Uses all twelve sounds in an octave.
- Aleatoric music. The composer uses electronic equipment to transmit the music.
- Minimalism. Repetition of rhythmic and melodic formulas with some variations.
Popular music
- Jazz. Has two main elements: rhythm and improvisation. Jazz para niños
- Rock and pop. Based on country and blues, with electric guitars, keyboard and drums. "Twist and shout" by The beatles.
- Incidental music. Sounds that add atmosphere to the action of a film, play radio/television programme or commercial.
- Piped music. Relaxing music for offices, shops and department stores.
- Commercial music. The music sold in shops or on the Internet. Music videos are used to advertise this type of music.








